1.Tax collected at source (TCS)
Tax collected at source (TCS) is the tax payable by a seller which he collects from the buyer at the time of sale. Section 206C of the Income-tax act governs the goods on which the seller has to collect tax from the purchasers.
2. Goods covered under TCS provisions and rates applicable to them
When the below-mentioned goods are utilized for the purpose of manufacturing, processing, or producing things, the taxes are not payable. If the same goods are utilized for trading purposes then tax is payable. The tax payable is collected by the seller at the point of sale.
The rate of TCS is different for goods specified under different categories :
3. Classification of Sellers and Buyers for TCS
There are some specific people or organizations who have been classified as sellers for tax collected at source. No other seller of goods can collect tax at source from the buyers apart from the following list :
1. Central Government
2. State Government
3. Local Authority
4. Statutory Corporation or Authority
5. Company registered under Companies Act
6. Partnership firms
7. Co-operative Society
8. Any person or HUF who is subjected to an audit of accounts under Income tax act for a particular financial year.
Similarly, only a few buyers are liable to pay the tax at source to the sellers.
Let us know who are those buyers:
1. Public sector companies
2. Central Government
3. State Government
4. Embassy of High commision
5. Consulate and other Trade Representation of a Foreign Nation
6. Clubs such as sports clubs and social clubs
4. TCS Payments & Returns
a. The dates for paying TCS to the government are :
*All sums collected by an office of the Government should be deposited on the same day of collection.
b. The seller deposits the TCS amount in Challan 281 within 7 days from the last day of the month in which the tax was collected.
c. Note: If the tax collector responsible for collecting the tax and depositing the same to the government does not collect the tax or after collecting doesn’t pay it to the government as per above due dates, then he will be liable to pay interest of 1% per month or a part of the month
d. Every tax collector has to submit quarterly TCS return i.e in Form 27EQ in respect of the tax collected by him in a particular quarter. The interest on delay in payment of TCS to the government should be paid before filing of the return.
5. Certificate of TCS
1. When a tax collector files his quarterly TCS return i.e Form 27EQ, he has to provide a TCS certificate to the purchaser of the goods.
2. Form 27D is the certificate issued for TCS returns filed. This certificate contains the following details:
a. Name of the Seller and Buyer
b. TAN of the seller i.e who is filing the TCS return quarterly
c. PAN of both seller and buyer
d. Total tax collected by the seller
e. Date of collection
f. The rate of Tax applied
3. This certificate has to be issued within 15 days from the date of filing TCS quarterly returns. The due dates are:
In case you are still confused about filing TCS returns, feel free to consult the tax experts at ClearTax.
6. TCS Exemptions
Tax collection at source is exempted in the following cases :
1. When the eligible goods are used for personal consumption
2. The purchaser buys the goods for manufacturing, processing or production and not for the purpose of trading of those goods.
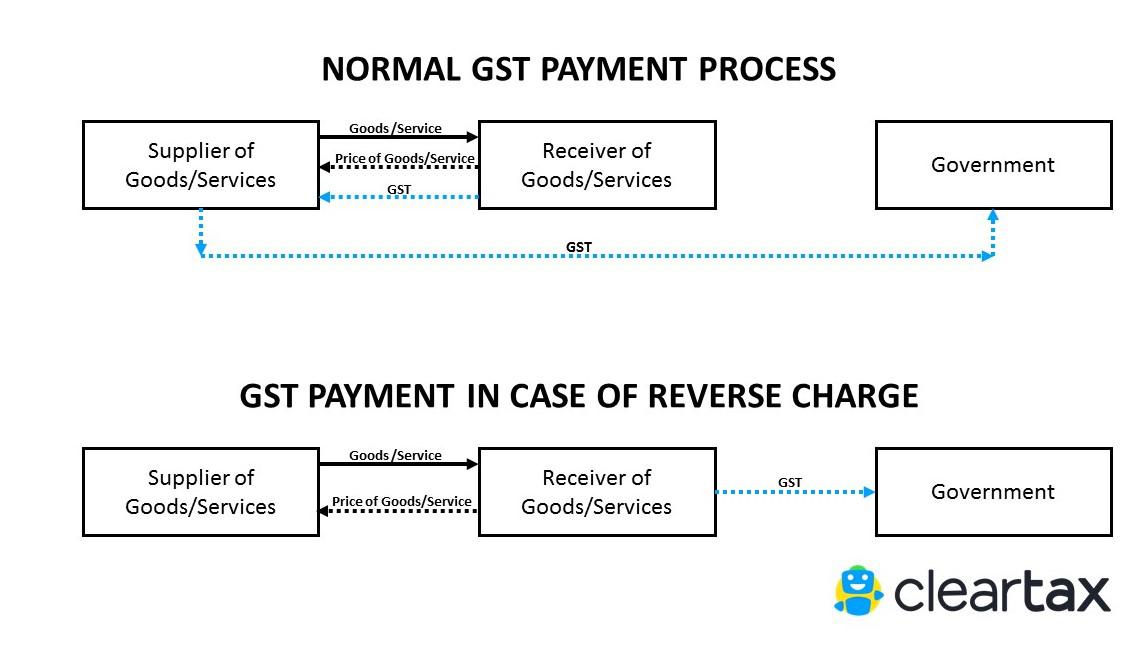
7. TCS under GST
a. Any dealer or traders selling goods online would get the payment from the online platform after deducting an amount tax @ 1 % under IGST Act. (0.5% in CGST & 0.5% in SGST)
b. The tax would have to be deposited to the government by 10th of the next month.
c. All the dealers/traders are required to get registered under GST compulsorily.
d. These provisions are effective from 1st Oct 2018.
Example: Mr. Raj(seller) is a trader who sells clothes online on Flipkart (buyer). He receives an order for Rs 10, 000 inclusive of commission. Flipkart would thus be deducting tax for Rs 100 (1% of Rs. 10000).
8. Submission of Form 24G
In case of an office of the Government, where tax has been paid to the credit of Central Government without the production of a challan associated with the deposit of the tax in a bank, below are the changes to the rules, Form 24G has to be submitted:
Rules where TDS is deposited without challan (changes to Rule 30)
a. If TDS has been deposited without a challan, the person to whom TDS has been reported for depositing to the government – such a person has to submit a statement in Form 24G to the agency authorised by the Principal Director of income tax (systems). [Rule 30(4)].
b. Such Form 24G must be submitted issued within 15 days from the end of the relevant month. For the month of March, the form should be submitted by 30 April 2019.
c. Form 24G must be submitted (a) electronically under digital signature (b) electronically along with verification in Form 27A (c) or verified through an electronic process as prescribed.
d. Person referred to in bullet 1 shall inform the Book Identification number generated to each of the deductors for whom the sum deducted has been deposited.
e. The Principal Director General of Income Tax (Systems) shall specify the procedure for furnishing and verification of statement Form 24G.
Rules where TCS under section 206C is deposited without challan (changes to Rule 37CA)
a. If TCS has been deposited without a challan, the person to whom the collector has reported the TCS for depositing to the government – such a person will submit Form 24G to the agency authorised by the Principal Director of income tax (systems).
b. Such Form 24G must be submitted within 15 days from the end of the relevant month.
c. If Form 24G pertains to month of March, it must be submitted on or before 30th April.
d. Form 24G must be issued (a) electronically under digital signature (b) electronically along with verification in Form 27A (c) or verified through an electronic process as prescribed.
e. Person referred to in bullet 1 shall inform the Book Identification number generated to each of the deductors for whom the sum deducted has been deposited.
f. The Principal Director General of Income Tax (Systems) shall specify the procedure for furnishing and verification of statement Form 24G.
www.cleartax.com